A Deep Dive Into Video Projectors: From Basics to Buying Guide
Introduction
Planning to buy a video projector? Or simply curious about this fascinating technology? Whether you're a tech enthusiast, a home theater enthusiast, or a business owner looking for presentation solutions, understanding what constitutes a video projector, how it works, and the fundamentals behind its operation might be essential. This comprehensive guide will breakdown these elements and provide insights on what to consider when buying a video projector.

What Is a Video Projector?
Are you intrigued by the world of video projectors? Before making a purchase or exploring this technology further, let's understand the fundamental nature of a video projector. Essentially, a video projector is an advanced device that replicates images produced by a computer source, such as a Blu-ray player, and casts them onto a larger surface.
These surfaces can be screens, walls, or other suitable surfaces. This device makes the everyday television set look small in comparison due to its ability to provide a substantially larger viewing size, a feature that makes it popular in places like classrooms, corporate meeting rooms, and home theaters.
Here's a simplified breakdown of a video projector:
- Source: A video Projector draws image data from sources like computers and Blu-ray players.
- Function: The projector uses a manufactured lens to cast light, enabling image magnification and projection.
- Versatility: Thanks to their substantial display size, projectors are perfect for group viewings, be it in classrooms, home theaters, or meeting rooms.
- Big Advantage: Video projectors offer a cinematic viewing sensation, transforming simple spaces into movie theaters within seconds.
With a basic understanding of a video projector, you're one step closer to making an informed choice or simply appreciating this technology better.
What is the Science Behind Video Projection?
The science behind video projection can be quite intimidating, yet intriguing. Pouring light on the underlying principles can educate potential buyers and tech enthusiasts on their operations. Video projectors utilize principles of optics and light, with an array of components contributing to image magnification, color reproduction, and brightness. Here are the critical elements:
- Light Source: In the heart of a projector is a high-intensity light bulb, or in some cases, a laser, that generates the light needed for image projection.
- Image Generation: Projectors employ one of three technologies - Liquid Crystal Display (LCD), Digital Light Processing (DLP) or Liquid Crystal on Silicon (LCOS) - to create an image. Each method manipulates light in a slightly different way to produce images.
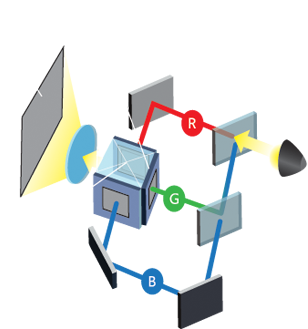
- LCD (Liquid Crystal Display): With LCD, light passes through special panels, each of which recreates a single color (red, blue or green). The colors combine to produce the final image.
- DLP (Digital Light Processing): Using DLP technology, light bounces off microscopic mirrors within a chip called a Digital Micromirror Device (DMD). As the light is reflected, it gets filtered through a color wheel to form the final colors of the projected image
- LCOS (Liquid Crystal on Silicon): LCOS is a hybrid technology that combines the benefits of both DLP and LCD. In LCOS, light bounces off a mirror, passes through a liquid crystal panel, and then reflects back towards the mirror to create the final image.
- Lenses System: Following image creation, projectors use a system of lenses to magnify the image and project it onto a screen.
- Color Wheels, Mirrors & Prisms: In DLP projectors, these elements play a critical role in producing vivid images.
Armed with this understanding of video projection science, choosing a projector becomes more about your specific requirements rather than relying solely on manufacturer specifications.
How Do Video Projectors Work?
Unraveling the magic behind video projectors involves understanding how they dissect images and utilize specific technologies to project them. Here's an overview:
- Disrupting Images: Initially, video projectors disrupt images into the primary colors of light: red, green, and blue. This breaking down is pivotal in creating the entire spectrum of colors in the resultant projection.
- Harnessing Technology: Video projectors mainly employ two types of technology - Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) or Digital Light Processing (DLP) - for manipulating light and eventually rendering the image.
- LCD-Based Process: In LCD projectors, each broken-down color component of the image encounters individual LCD panels. These panels control the amount of light passing through them, either allowing it or blocking it selectively. This manipulation effectively recreates the image.
- DLP-Based Process: DLP projectors take a slightly different approach. A light source bounces off microscopic mirrors found on a Digital Micromirror Device (DMD). The reflected light then filters through a color wheel during projection onto the screen.
Regardless of whether they are LCD or DLP, both types can generate clear, vibrant images, turning any space into a mini theatre. Their magic lies in their precision in controlling light, playing with primary colors, and using mirrors and panels to create life-like images. With each passing year, advancements in this technology continue to enhance the sophistication and clarity of video projectors, paving the way for increasingly immersive viewing experiences.
What Are the Different Types of Video Projectors?
When considering video projection technology, three primary types stand out owing to their distinct mechanisms and output. These are DLP (Digital Light Processing), LCD (Liquid Crystal Display), and LCOS (Liquid Crystal on Silicon).
1. DLP (Digital Light Processing):
- _Mechanism_: Uses minute mirrors coupled with a spinning color wheel to create images.
- _Advantages_: Known for their high-contrast levels and reduced pixelation, which result in sharper images.
- _Downside_: They can produce a rainbow effect in fast-moving or high-contrast scenes.
2. LCD (Liquid Crystal Display):
- _Mechanism_: Functions by passing light through specialized glass panels to generate images.
- _Advantages_: Recognized for their color accuracy and image clarity, they are perfect for rooms with controlled ambient light.
- _Downside_: Tend to have lesser black level performance which impacts the contrast ratio.
3. LCOS (Liquid Crystal on Silicon):
- _Mechanism_: Offers a hybrid version of DLP and LCD technology.
- _Advantages_: Provides superior image quality with high-resolution display and improved color accuracy.
- _Downside_: Devices utilizing this technology are usually the most expensive.
In making your selection, consider not only the image quality each type offers but also other factors such as cost, the device's purpose, and the environment in which it will be used. One might be superior to another in a specific aspect, but the best projector for you depends on your personal and professional needs. Remember, all types of projectors are capable of delivering a satisfactory performance under the right conditions.
What Should I Consider When Purchasing a Video Projector?
Selecting a video projector can be a overwhelming task due to the numerous models and specifications available on the market. This section provides a clear outline of significant factors to consider when choosing a video projector:
- Purpose of the Projector: Establish whether you're purchasing the projector for home cinema, business presentations, or school use. These settings demand different projector features.

- Projector's Resolution: If home cinema is your primary goal, ensure the projector supports Full HD or 4K resolution. This promises sharper images and a more immersive viewing experience.
- Brightness Level: This factor is measured in lumens. Generally, a higher lumen rating signifies a brighter display. If you plan to use the projector in a well-lit room, opt for a projector with higher lumens.
- Contrast Ratio: This defines the difference between the darkest and the brightest parts of the image. Higher contrast ratios deliver more vibrant and realistic images.
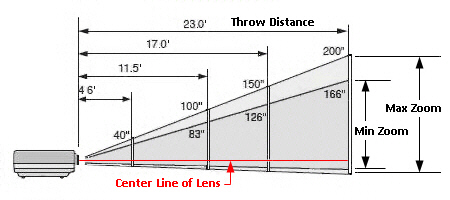
- Throw Distance: This refers to the maximum image size a projector can display at a specific distance. Depending on the size of your room, choose between a short-throw or a long-throw projector.
- Connectivity Options: If your work involves presentations, you might need a projector with wireless connectivity for convenience.
- Type of Bulb: Check the type of bulb used in the projector. LED bulbs, for instance, have a longer life but may not be as bright as traditional projector lamps.
- Lamp Life and Replacement Cost: Projector lamps age over time. Longer lamp life means lower running costs. Additionally, factor in the cost of potential lamp replacements.
Remember that the activity of finding the best video projector should not only revolve around the cost but also meeting your specific usage requirements.
Conclusion
Ultimately, video projectors offer an ideal solution for most big-screen viewing needs, whether it's for business presentations, educational purposes, or home theater systems. The technology behind it is complex yet fascinating, and understanding this can help you make an informed purchase. Remember, the best projector is not always the most expensive, but the one that best suits your specific needs and circumstances.
Related FAQs about what is a video projector
How does an LCD projector differ from a DLP projector?
LCD projectors pass light through three individual LCD panels to recreate the image, while DLP projectors bounce light off numerous tiny mirrors and filter it through a color wheel to form the images. Both methods can result in bright, clear images, but each has its advantages and disadvantages in terms of color accuracy, contrast levels, and possible visual effects.
How can I optimize the performance of my video projector?
Ensure the projector's lens is clean, setup proper room lighting, use a compatible screen, adjust the projector's contrast, and brightness settings. Regularly changing the bulb when it ages also improves performance. It's ideal to consult your projector's manual for specific settings and maintenance instructions.
What are some reliable brands to consider when buying a video projector?
Reliable brands for video projectors include Epson, Optoma, BenQ, and Sony. These brands have various models to choose from, ranging from affordable options for casual use to higher-end models for professional or home theater setups. Ultimately, the best brand will depend on your specific projection needs and budget.